생물학의 분야인 유전학(genetics)은 살아있는 생명체의 유전(heredity)과 변이(variation)의 과학이다. 역사이전 시대부터 살아있는 것은 그들의 부모로부터 특성을 물려받는다는 사실을 알고 선택적 교배를 통해서 작물과 동물을 향상시켰다. 그러나, 유전학의 새로운 과학은 유전의 과정을 이해하는 것으로, 19세기 중반에 그레고르 멘델(Gregor Mendel)에 의해 처음 시작되었다. 비록 멘델은 유전에 대한 물리적인 기본을 알지 못했지만, 그는 생명체의 유전 특성이 분리되어 있다는 특성을 발견했다. 이들 기본적인 유전의 단위를 오늘날 유전자(gene)라 부른다.
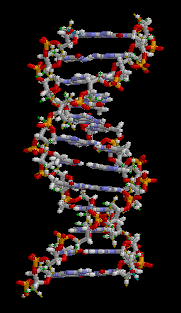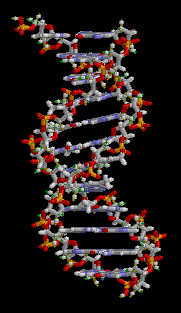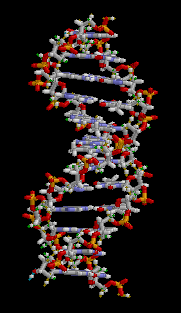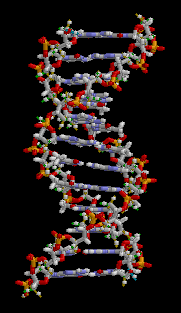
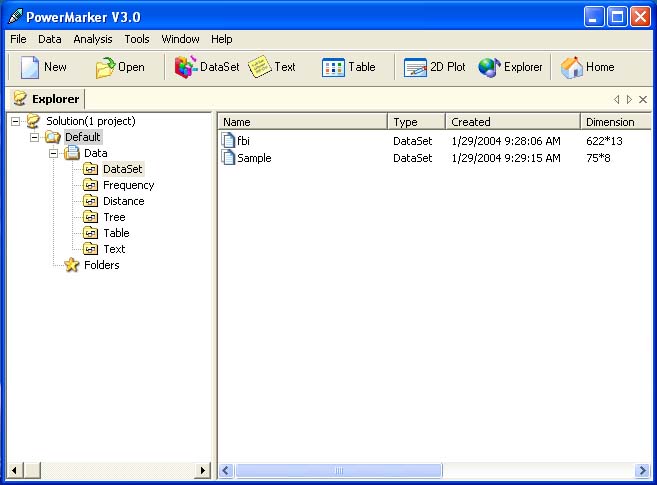
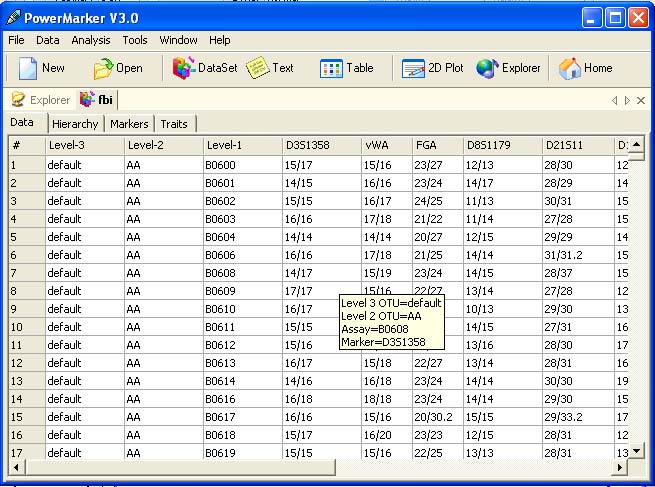
유전학은 유전의 기본 단위인 유전자의 연구를 통해서 유전, 유전적 변이 그리고 선택적 교배를 다루는 생물학의 한 가지이다. 유전자는 네 종류의 뉴클레오티드(nucleotide)의 사슬로 구성된 분자인 DNA안에 상응하는 영역이다. - 이들 뉴클레오티드의 서열은 생명체가 물려받는 유전적 정보이다. DNA는 기본적으로 서로 상보성(complementary)을 띠는 각 사슬의 뉴클레오티드와 함께 이중 가닥 형태를 나타낸다. 각 사슬은 새로운 파트너 가닥을 만드는 주형(template)으로 작용할 수 있다. - 이것은 유전자의 사본을 만들어서 유전될 수 있도록 하는 물리적 방법이다.
유전자에 있는 뉴클레오티드의 서열은 세포에 의해 번역되어 아미노산의 사슬을 생산하고 단백질을 만든다. - 단백질에 있는 아미노산의 순서는 유전자에 있는 뉴클레오티드의 순서와 대응한다. 이것은 유전 암호(genetic code)라고 알려져 있다. 단백질 내의 아미노산은 3차원 형태로 접힘(fold)으로써 정의된다.; 이 구조는 단백질이 기능을 나타낼 수 있도록 한다. 단백질은 세포가 살아가기 위해 필요한 거의 모든 기능을 수행한다. 유전자에 있는 DNA의 변화는 단백질의 아미노산에 변화를 일으킬 수 있고, 단백질의 형태와 기능을 변화시킨다.; 이것은 세포와 전체 생명체에 극적인 영향을 줄 수 있다.
비록 유전학이 생명체의 행동을 나타내는데 큰 역할을 하지만, 그것은 생명체가 경험한 것과 함께 유전학이 결합하여서 궁극적인 결과를 정한다. 예를 들어, 유전자가 사람의 키, 영양과 건강을 정하는 역할을 하지만, 어린시절의 경험 또한 큰 영향을 주게 된다.
유전학(genetics)은 살아있는 생명체가 어떻게 그들 선조의 수많은 특성을 전달하는지에 대해 연구한다. - 예를 들면, 아이들이 보통 그들 가족의 다른 사람들처럼 보고 행동하는 것과 같은 것이다. 유전학은 유전된 특성을 확인하기 위해 노력하고, 구체적으로 어떻게 이들 특성이 세대에서 세대로 전달되는지 연구한다.
유전학에서, 생명체의 특성을 "형질(trait)"이라 부른다. 몇몇 형질은 생명체의 물리적 외형의 특성들이다. 사람의 눈 색, 키 또는 몸무게 등을 예로 들 수 있다. 많은 다른 형태의 형질과 질병에 저항하는 반응 양상의 범위가 존재한다. 형질은 종종 유전된다. 예를 들면, 키크고 날씬한 사람은 키크고 날씬한 자녀를 갖는 경향이 있다. 다른 형질은 유전된 특성과 환경 사이의 상호작용으로부터 나타난다. 예를 들어, 아이가 키가 큰 경향으로 유전되었지만 만약 그가 사는 곳에 음식이 적고 궁핍하게 자랐다면, 키가 작을 것이다. 유전학과 환경이 상호작용하여 형질을 만드는 과정은 이해하기 어려울 수 있다. : 예를 들면, 누군가가 암 또는 심장병으로 죽을 확률은 그들의 가족력과 생활양식 두가지에 의존해서 판단한다.
유전 정보는 DNA라 부르는 긴 분자에 의해 운반되고 이 DNA는 세대를 거쳐서 복제되고 전달된다. 형질은 생명체를 구성하고 운영하기 위한 지시사항으로써 DNA로 운반된다. 이들 지시사항은 유전자라 부르는 DNA의 조각에 포함되어 있다. DNA는 유전 암호에 있는 지시사항을 한자한자 읽어가는 이들 단위의 상태와 함께 간단한 단위의 서열로 구성된다. 이것은 단어를 한자한자 나열한 편지의 상태와 유사하다. 생명체는 이러한 단위의 서열을 읽고 지시사항을 해독한다.
특정 지시사항에 대해 존재하는 유전자가 똑같지는 않다. 유전자의 한 유형의 다른 형태를 그 유전자의 다른 대립인자(allele)라고 부른다. 그 예로써, 머리 색에 대한 한 유전자의 한 대립인자는 검은 머리카락에서 많은 색소를 생산하는 지시사항을 운반하는 반면, 다른 대립인자는 이 지시사항의 잘못된 버전을 줄 수 있고, 그래서 색소를 생산하지 않고 머리카락이 하얗게 된다. 돌연변이(Mutation)는 유전자의 서열이 변하고 따라서 새로운 대립인자가 생기는 무작위적인 사건이다. 돌연변이는 검은 머리카락에 대한 대립인자를 흰 머리카락에 대한 대립인자로 바꾸는 것과 같이 새로운 형질을 만들 수 있다. 새로운 형질의 출현은 진화에서 중요하다.
- 출처 : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetics
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Introduction_to_genetics
'[BT]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 랩에 있는 사람만 아는 이야기들...ㅋㅋ (0) | 2008.12.11 |
|---|---|
| Genetics glossary (유전학 용어집) (0) | 2008.07.02 |
| DNA Compaction 동영상 (0) | 2008.07.01 |
| Transcription and Translation 동영상 (0) | 2008.07.01 |
| The Inner Life of The Cell (0) | 2008.07.01 |