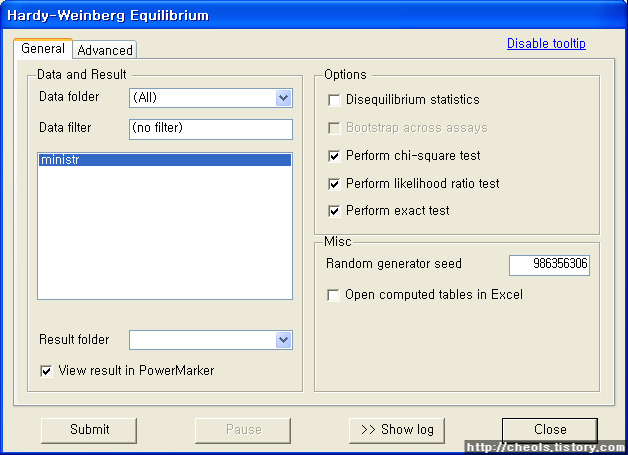
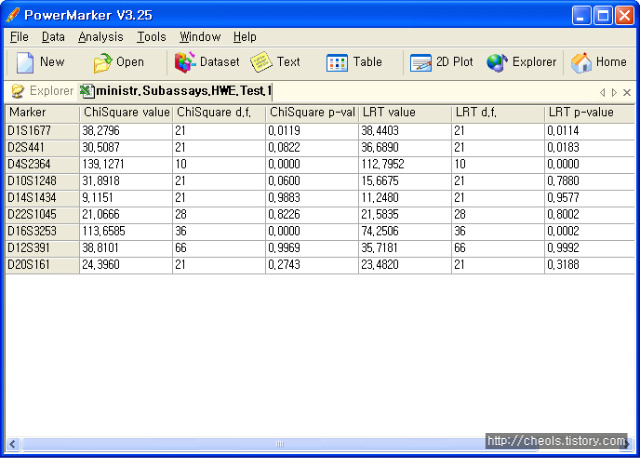
The D-statistic was introduced in Green et al. (2010) (Neandertal admixture paper) and used in Reich et al. (2010) (Denisovan admixture paper). In basic terms it studies whether from a pair of populations P1, P2 one is closer to a third one P3, using P4 as an outgroup.D(P1,P2,P3,P4)
In the aforementioned papers it was usually used like this:
D(Eurasian, African, Archaic, Chimpanzee)and its positive values were interpreted as evidence of archaic admixture of different kind in subsets of modern humans (non-Africans and Melanesians).
블로그를 구경하다가 D-statistics 라는 것을 보았습니다. 저도 처음 보는 것이라 한번 보면서 간단히 소개하고자 합니다.
D-statistics는 2010년에 Green 등 (2010)과 Reich 등 (2010)에 의해 처음 소개되었습니다. 이 방법은 기본적으로 한 쌍의 집단 P1, P2 그리고 비교할 세 번째 집단 P3, outgroup(외부집단)으로 이용되는 P4 를 이용해서 조사하며, 이는 D(P1,P2,P3,P4)로 표시합니다.
예를 들어 D(Eurasian, African, Archaic, Chimpanzee)일 때 결과값이 positive한 값이면, 현대 인류의 일부에 다른 종의 고대의 혼합이 있다는 증거로 해석할 수 있습니다.
고대 DNA 분석을 위한 목적으로 최근에 나온 방법이며, 집단간에 혼합의 정도를 분석하는 방법중 한 가지 입니다.
아직 처음 본거라 정확한 내용은 더 공부해야 알 듯 합니다. 추가적인 내용은 아래 출처를 참조해주세요.
- 출처 : Dienekes' Anthropology Bolg, Mol Biol Evol (2011) doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr048
'[BT] Population and forensics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Y-chromosome haplogroups 세계지도 (0) | 2013.09.16 |
|---|---|
| “한민족 뿌리는 이주 농사꾼”유전적 연구로 근거 찾았다 (0) | 2011.05.25 |
| 하플로그룹 (Haplogroup) 이란? (0) | 2011.04.05 |
| DNA 프로파일링 (DNA profiling) (0) | 2011.04.05 |
| [펌] 한국인의 핏줄, 누구와 더 가깝나? (3) | 2010.03.15 |